Enhancing Safety and Sound Insulation with Laminated Glass Windows and Doors
- Share
- Issue Time
- Mar 28,2024
Summary
Laminated glass has emerged as a top choice for custom windows and doors, offering not only enhanced safety but also superior sound insulation properties.
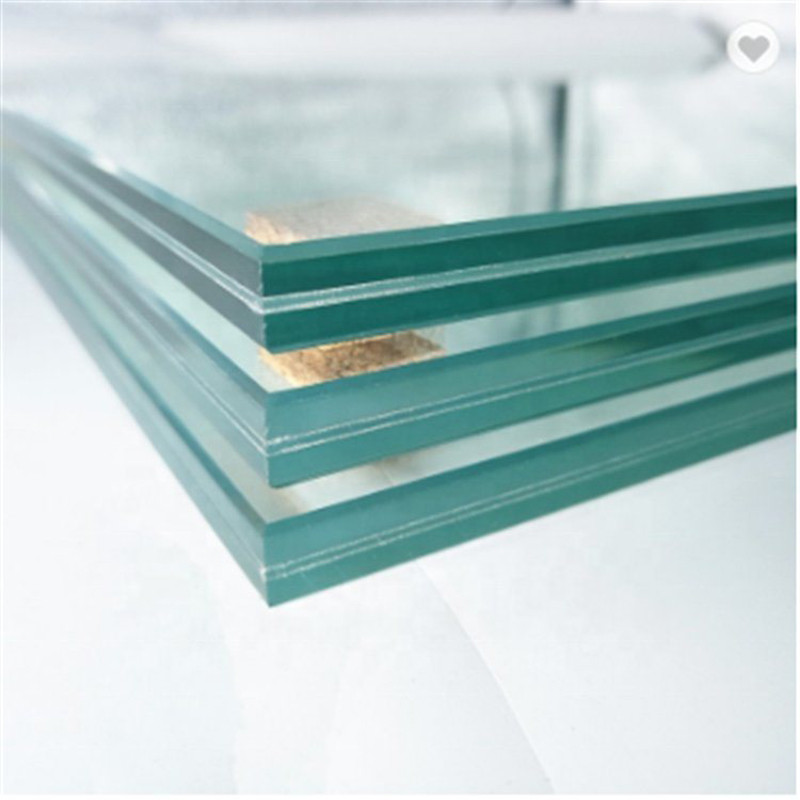

Laminated glass has emerged
as a top choice for custom windows and doors, offering not only enhanced safety
but also superior sound insulation properties. In this article, we'll delve
into the benefits of laminated glass in improving safety and reducing noise
transmission, making it an ideal choice for residential and commercial
applications.
What
Is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is made by sandwiching a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) layer of thin plastic between two panes of annealed glass and fusing them together. The interlayers work to support and hold the glass to create a strong, uniformed layer even when broken. Laminated glass comes in varying thicknesses and can be created using different glass combinations or coatings to provide different qualities, such as low emissions or increased insulation.
How Is Laminated Glass Made?
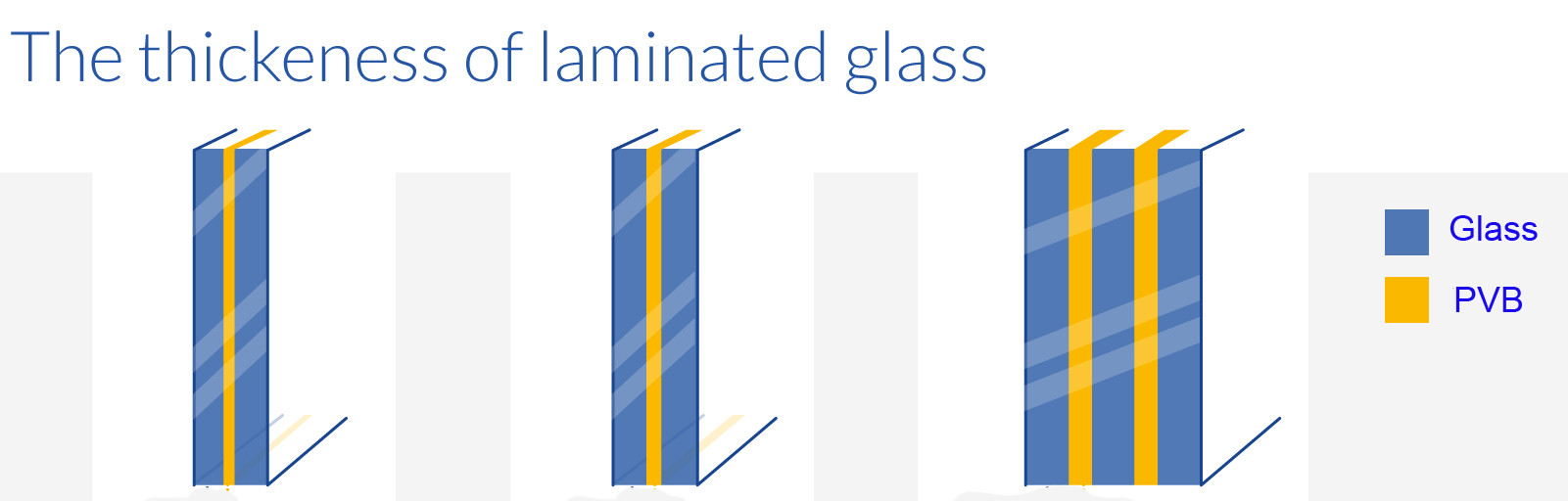
Laminated glass can be manufactured in many ways for differences in the final product:
Glass used (standard annealed, toughened)
Thickness and number of plies
The interlayer material (PVB is the most popular)
For security purposes, the glass can be made in different thicknesses with different interlayers specifically for either:
Bullet resistance
Forced entry resistance
Hurricane Impact
The layers or plies are assembled together in a controlled environment and vacuum extraction removes the air between the layers. The sheet is heat treated, compressed and then placed in an autoclave before final inspection.
The PVB interlayer used for domestic laminated glass is made in multiples of 0.38mm with standard thickness being 0.76 mm, 1.14 mm, 1.52 mm and 2.28 mm
For non-domestic uses, the glass can be made from multiples of plies with different types of interlayer material in different thicknesses. For example, the cockpit of an aeroplane has five plies fused together and the interlayer ply is 2.60 mm thick compared to 0.76 of a standard domestic window.
Laminated Glass Windows and Doors Benefits
Safety Advantages
One of the primary reasons for the widespread adoption of laminated glass windows and doors is its exceptional safety features. Unlike traditional glass, which shatters into sharp fragments upon impact, laminated glass remains intact due to its layered construction. The interlayer between the glass layers holds the fragments together, reducing the risk of injury from flying shards. This makes laminated glass windows and doors a safer choice, especially in environments where safety is a priority, such as homes with children or public buildings.
Impact Resistance
Laminated glass windows and doors is designed to withstand impacts, making it highly resistant to breakage. This property is particularly valuable in areas prone to severe weather conditions or potential break-ins. In the event of an attempted break-in, laminated glass provides an additional barrier, as it is difficult to penetrate even if the outer layer is shattered. This adds an extra layer of security to homes and businesses, giving occupants peace of mind.
Sound Insulation Benefits
Apart from its safety advantages, laminated glass windows and doors excels in sound insulation, creating a quieter and more comfortable indoor environment. The multi-layered structure of laminated glass effectively absorbs and dampens sound waves, reducing noise transmission from outside sources such as traffic, construction, or loud neighbors. This makes laminated glass windows and doors an excellent choice for locations where noise pollution is a concern, allowing occupants to enjoy a peaceful living or working environment.
UV Protection
The PVB interlayer will reduce UV transmission to stop the damage to furnishings and furniture, especially in south-facing windows.
How Laminated Glass Works for Sound Reduction?
Laminated glass is used in noise reduction windows as it helps to dampen the sound.
Noise reduction windows can reduce soundwaves because they have a gap between the panes of glass filled with Argon gas that reduces the transmission of the wave.
By using a laminated layer on one pane of glass in the double-glazed unit, the panes have different widths and this is enough to cause the panes to oscillate at different vibrations.
The difference in frequency disrupts the soundwave and reduces the transference of noise through the glass. The PVB laminated layer can also dampen the sound transference through the pane of glass.
All of these factors combined can help to reduce noise by up to 40 dB
How Laminated Glass Works for UV Resistance?
Laminated glass also has the benefit of reducing UV light transmission.
UV bleaching is also known as colour fading or photodegradation, where ultraviolet light causes a change in molecular structure that reduces pigment.
Sunlight, as warming and uplifting as it is, can cause damage to fabrics, furnishings and floors where the intense light shines. Wooden floors can warp, leather settees crack and artwork can fade. This is especially a problem for windows that face south or southwest and are exposed to sunlight at its most intense during the day.
The PVB layer in laminated
glass does reduce UV transmittance considerably compared to standard glass and
helps to protect furniture and furnishings.
Laminated glass windows and
doors offer a multitude of benefits, from enhanced safety and security to
superior sound insulation and energy efficiency. Contact us today to get your right
glass for your windows and doors.